If you hear or read a new word you can look up at a dictionary to learn what it means. It's easy. But often the opposite happens - you want to find a particular word that means something and the dictionary can't help you. A word lingers at the tip of your tongue but you just can't get it. You know you know the word but you can't recall it. It's frustrating. In such moments, OneLook's Reverse Dictionary will come to your rescue.
OneLook's reverse dictionary lets you describe a concept, the meaning of the word and it shows you a list of words and phrases that fits the description. Your description can consist a few words, a sentence, a question, or even just a single word. OneLook will display a whole lot of words relating to the description with words with the best matches at the top. Clicking on the words will show you links to other online dictionaries where you can look up it's meaning.
I tried a few. "A mistake resulting from inattention", I typed and it brought me these.
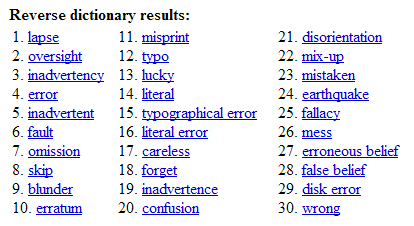
"lack of information" brought equally good results.
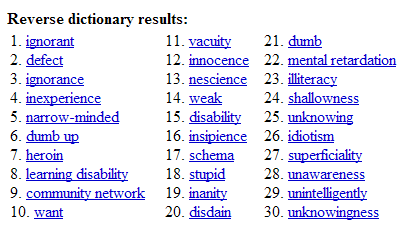
Often, it would display lots of unrelated words, but it does no harm to get more results. It might even turn out that a word way down the list is more befitting to the context than the ones at the top.
The reverse dictionary supports different types of wildcards.
- The asterisk (*), one of the most common wildcards can be used to find words with certain sequence of alphabets. You already know it.
- The question mark (?) is another wildcard that matches exactly one character. The difference between the asterisk and question mark is that the asterisk can match any number of characters while one question mark represents only one character.
- The sign (#) matches any English consonant. For example, the query "tra#t" finds the word "tract" but not "trait".
- The sign (@) matches any English vowel. For example, the query abo@t finds the word "about" but not "abort".
- You can combine two or more wildcards to get specific results. For example, the query "b*:food" will find all words beginning with b and related to food.
- You can find phrases by flanking a word with two asterisks to the left and to the right. For example, the query **bird** will show you all phrases with the exact word bird in it.
- You can expand acronyms by using the parameter "expand:" as in expand:UNO
Reverse dictionary is amazingly useful.

Comments
Post a Comment