The model number of a hard disk can reveal a lot of information about the drive if you know how to read it. Understanding the naming convention used by different hard disk manufacturer will allow you to know the features and specification of the drive by just glancing at the model number. You won’t have to search on the Internet to learn about the drive. Shopping for drives will become easier because you have all the information on the go.

As I said, different hard drive manufacturers employ different naming techniques. Let’s look at some of the popular hard drive manufacturers.
Seagate
A sample model number: ST3750640AS
Breaking it up into a readable form:
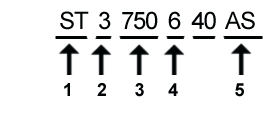
- ST stands for the Company initials, “Seagate Technology”. STM stands for “Seagate Technology Maxtor”
- Form factor (3 = Standard 3.5 inch drives, 9 = 2.5 inch Laptop drive)
- Total Capacity in Gigabytes (1000MB = 1GB). This is a 750GB drive.
- Cache Size (0 = 2MB, 2 = 2MB, 3 = 8MB, 4 = 16MB, 6 = 16MB, 8 = 8MB)
- Connector Interface type (A = 40pin PATA and AS = SATA interface)
Western Digital
A sample model number: WD5000AAKS
Breaking it up into a readable form:
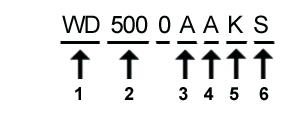
- WD: Company initials, “Western Digital”
- Drive capacity in Gigabytes.
- Form factor. GB stands for Gigabyte and TB for Terabyte
A = 3.5-inch GB
B = 2.5-inch GB
E = 3.5-inch TB
F = 3.5-inch TB (new format) - Business Unit or Brand
A = Desktop/WD Caviar
B = Enterprise/WD RE2 (3-platter)
C = Desktop/WD Protege
D = Enterprise/WD Raptor
E = Mobile/WD Scorpio
H = Enthusiast/WD Raptor X
V = Audio/Video - WD AV
Y = Enterprise/WD RE2 (4-platter) - RPM/Buffer Size or Attribute
F = 10,000 RPM with 16 MB cache
G = 10,000 RPM with 8 MB cache
J = 7200 RPM with 8 MB cache
K = 7200 RPM with 16 MB cache - Interface Connector
D = SATA 1.5 Gb/s with 22-pin SATA connector
E = ATA/133 with 40-pin IDE connector
S = SATA 3.0 Gb/s with 22-pin SATA connector
Hitachi
A sample model number: HDS722516VLAT20
Breaking it up into a readable form:
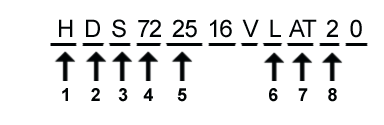
- Company initial “Hitachi”
- Product Family:
D = Deskstar
C = CinemaStar
T = Travelstar
U = Ultrastar
M = Microdrive
E = Endurastar - Series prefix:
S= Standard (default, if no series name prefix)
C = Compact - Speed, expressed in Revolutions Per Minute (rpm):
72 = 7200 rpm
10 = 10,000 rpm
15 = 15,000 rpm - Disk capacity
25 = 250GB (first two significant digits)
50 = 180GB etc... - Form factor (height)
L = 1"
7 = 7 mm
9 = 9.5 mm
5 = 5 mm
8 = 8 mm - Interface:
A3 = Serial-ATA 3 Gbit/s
SA = Serial-ATA 1.5 GBit/s
AT = ATA - Cache size in MB
You must have noticed that I left out certain characters in the model numbers. Those are unique numbers specific to the manufacturer that doesn’t represent any information that the user can use. For instance, in the Hitachi model 16, V and the concluding 0 are unique codes.
The model names does look complex and would probably be hard to learn them by heart. But you won’t need to remember them all, because you only need to find out some particular information like disk capacity, RPM speed and the cache. The interface you can find out by just looking at the connector. The 1.5 Gbit/s SATA drives are almost obsolete and also the 5400 RPM disks (hence I didn’t even include codes for 5400 RPM disks).
Sources:Seagate, Hitachi, Western Digital

Comments
Post a Comment